Finding blood after a bowel movement can be an alarming experience. While rectal bleeding should always be evaluated by a specialist, the most frequent culprit is a common condition: internal hemorrhoids.
Internal hemorrhoids commonly cause bright red rectal bleeding due to increased pressure, thinning of the vessel walls, and chronic inflammation.
Ongoing bleeding can lead to iron-deficiency anemia, and conservative therapies often fail to address the underlying vascular issue, while traditional surgery can be painful with a long recovery.
Hemorrhoid Artery Embolization (HAE) is a minimally invasive treatment that reduces blood flow to hemorrhoids, shrinking them and stopping bleeding with quick recovery and minimal discomfort. A specialist evaluation is essential to confirm the cause of bleeding and determine the best treatment.
What Are Internal Hemorrhoids?
Hemorrhoids are not “abnormal” growths; they are pillow-like clusters of veins located in the lower rectum and anus. They serve as cushions to support bowel control. However, when these veins become swollen or inflamed, they develop into the condition we commonly call hemorrhoids.
Internal hemorrhoids develop inside the rectum. Because there are fewer pain-sensing nerves in this area, you might not feel them, but they are the primary source of bright red rectal bleeding.
Why Do Hemorrhoids Bleed?
The mechanics of hemorrhoidal bleeding are relatively straightforward, yet they point to a significant underlying vascular issue.
1. Increased Venous Pressure
The veins in the rectal area are highly sensitive to pressure. When you strain during bowel movements (often due to constipation), the pressure causes these veins to engorge and stretch.
2. Thinning of the Vessel Walls
As internal hemorrhoids swell, the tissue covering them becomes stretched and thin. When stool passes through the rectum—especially if it is hard—it can scrape or rupture these delicate, high-pressure vessel walls. This results in the characteristic bright red blood seen on toilet paper or in the bowl.
3. Chronic Vascular Inflammation
If left untreated, the constant cycle of swelling and irritation prevents the vessels from healing. This is why many patients experience “flares” where bleeding stops for a few days, only to return more aggressively later.
The Link Between Hemorrhoids and Chronic Anemia
It is a common misconception that minor rectal bleeding is harmless. When internal hemorrhoids bleed regularly, the cumulative loss of blood can lead to iron-deficiency anemia.
Patients should be aware of the systemic signs of blood loss, which include:
- Unexplained fatigue or lethargy.
- Dizziness or lightheadedness.
- Shortness of breath during routine activity.
If you are experiencing these symptoms alongside rectal bleeding, a vascular evaluation is necessary to determine if the blood loss is impacting your systemic health.
Evaluating Treatment Pathways
For decades, patients were given two extreme choices:
- Conservative Care: Creams, ointments, and fiber supplements. These manage symptoms but do not fix the underlying vascular problem.
- Hemorrhoidectomy: A painful surgical “cutting” procedure that requires a long, uncomfortable recovery.
Rather than face the recovery time of traditional surgery, many patients choose to suffer in silence. Recent advancements in interventional radiology have introduced Hemorrhoid Artery Embolization (HAE), a procedure that addresses the underlying arterial pressure without the need for surgical excision.
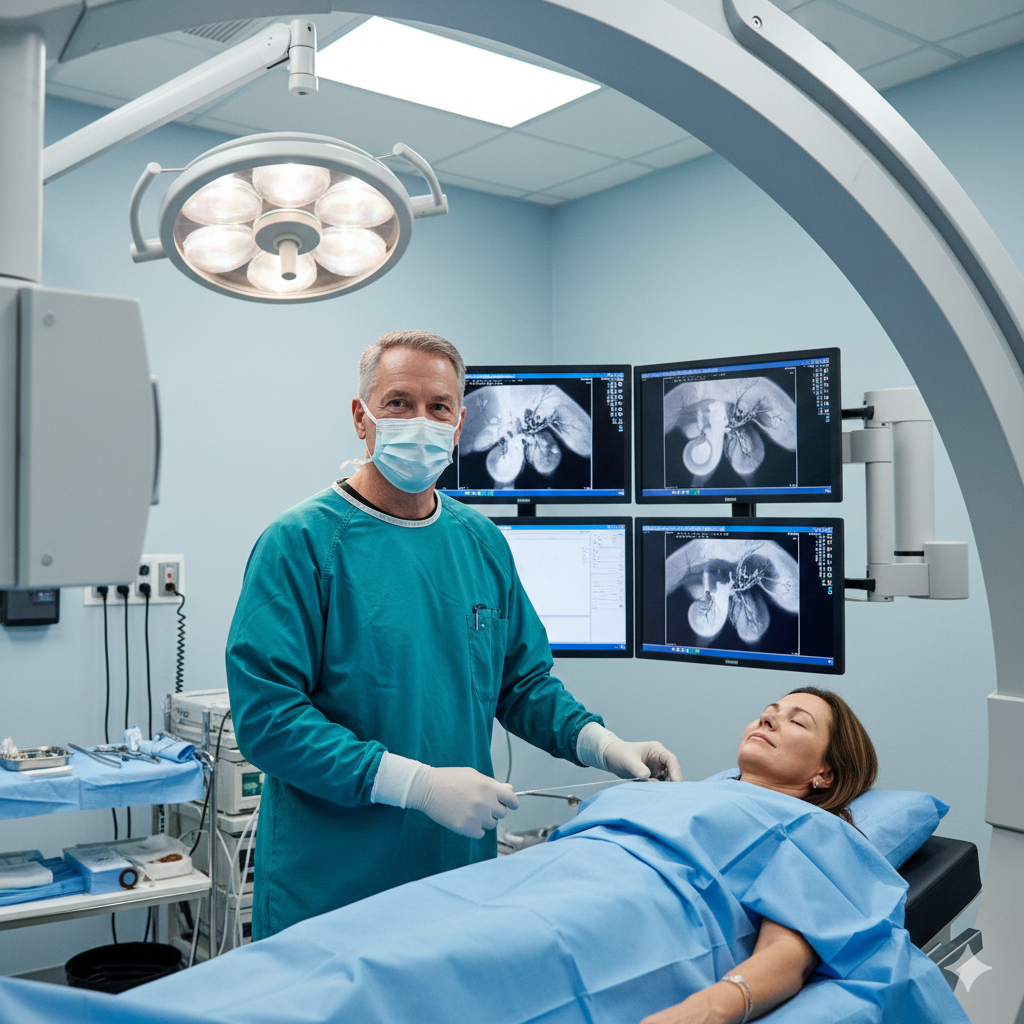
Hemorrhoid Artery Embolization (HAE): A Vascular Approach
If your hemorrhoids are bleeding, it’s because they are receiving too much blood flow under too much pressure. Hemorrhoid Artery Embolization (HAE) treats the problem at the source.
How HAE Works:
HAE is a minimally invasive outpatient procedure performed by an interventional radiologist.
- Arterial Access: A physician makes a microscopic incision, typically in the wrist or groin, to access the arterial system.
- Precision Navigation: Using advanced fluoroscopic imaging, a microcatheter is navigated to the superior rectal artery.
- Embolization: Small, medical-grade microspheres are deployed into the specific arterial branches feeding the hemorrhoids. This reduces the arterial pressure and “calms” the blood flow.
- Resolution: Without the excessive pressure, the hemorrhoidal tissue shrinks naturally, and the risk of vessel rupture is significantly reduced.
Without the high-pressure blood supply, the hemorrhoid shrinks naturally and the bleeding stops. There is no cutting, no stitches, and no hospital stay.
Benefits of HAE over Surgery:
- Quick Recovery: Most patients return to normal activities within a day or two.
- Minimal Discomfort: Since there is no surgical incision in the sensitive rectal area, the post-procedure pain is significantly lower.
- High Success Rate: HAE is highly effective at stopping the persistent bleeding that characterizes Grade 2 and Grade 3 internal hemorrhoids.
What to Expect in the Procedure Room During HAE
While the technical details of Hemorrhoid Artery Embolization (HAE) may seem complex, the patient experience is designed for comfort and minimal stress. You will lie comfortably on a procedure table, typically under conscious sedation—meaning you’ll be deeply relaxed, possibly even napping, but able to respond if needed. Our interventional radiologists utilize advanced imaging equipment, such as a C-arm, to visualize the superior rectal artery. You won’t see graphic images; instead, our specialists will be focused on real-time X-ray “road maps” of your blood vessels. A small access site, often in the wrist, is prepped, and sterile drapes ensure a safe environment while the physician carefully guides a thin catheter to the target vessels. The entire focus is on precision and your comfort.
When to See a Specialist
While internal hemorrhoids are a leading cause of rectal bleeding, it is vital to confirm the diagnosis with a specialist. You should schedule an evaluation if you experience:
- Persistent or recurring bleeding.
- A sensation of “fullness” or a prolapsed internal hemorrhoid.
- Symptoms of anemia, such as chronic weakness.
- Ineffectiveness of over-the-counter rectal bleeding treatments.
You Don’t Have to Live With the Bleeding
At USA Hemorrhoid Centers, our goal is to help patients understand the underlying vascular mechanics of this condition. By identifying the cause of the bleeding—rather than just treating the surface symptoms—we can offer more effective, long-term solutions with Hemorrhoid Artery Embolization (HAE).
Our facilities maintain rigorous standards of safety and excellence, earning accreditation from the Accreditation Association for Ambulatory Health Care (AAAHC). This distinction reflects our ongoing commitment to high-quality, patient-centric vascular care. To ensure our treatments remain accessible, we accept a wide range of insurance providers and offer several flexible payment programs.
The Importance of Early Intervention
If you are experiencing symptoms of internal hemorrhoids, a formal clinical evaluation is recommended. Seeking treatment in the early stages is the most effective way to prevent acute complications, such as a burst hemorrhoid or rupture. Our specialists focus on proactive care to mitigate the risks associated with chronic hemorrhoids, including prolapse, infection, and debilitating pain.

