Bleeding during a bowel movement and anal discomfort are symptoms of two common and seemingly similar conditions: hemorrhoids and anal fissures.
It’s easy to confuse the two if you look at symptoms alone. Often, a medical exam is the only way to determine for sure if anal bleeding, irritation, and other issues are caused by anal fissures or hemorrhoids. Knowing the difference can determine what treatment will offer relief and what prevention strategies will help you avoid future problems.
USA Hemorrhoid Centers is an expert in non-surgical hemorrhoid treatment. This guide explains the difference between hemorrhoids and anal fissures and what to do if you think you have symptoms caused by one of these conditions.
Schedule A Hemorrhoid Consultation
What’s the Difference Between Hemorrhoids and Anal Fissures?
The difference between hemorrhoids and anal fissures is that hemorrhoids impact veins in or near the anus, and anal fissures are tears in the anal tissue.
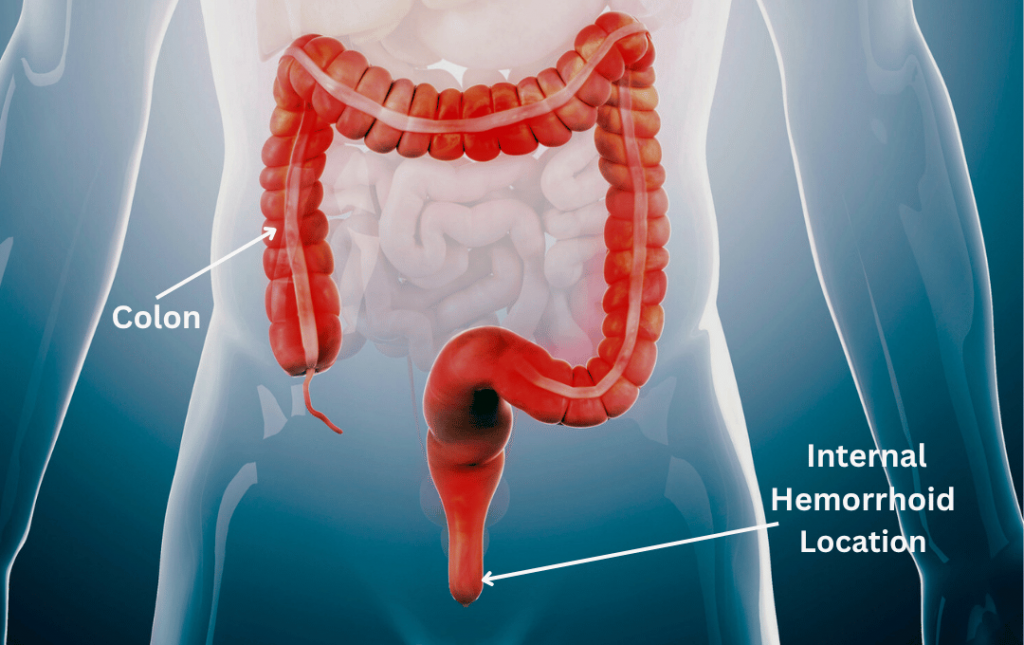
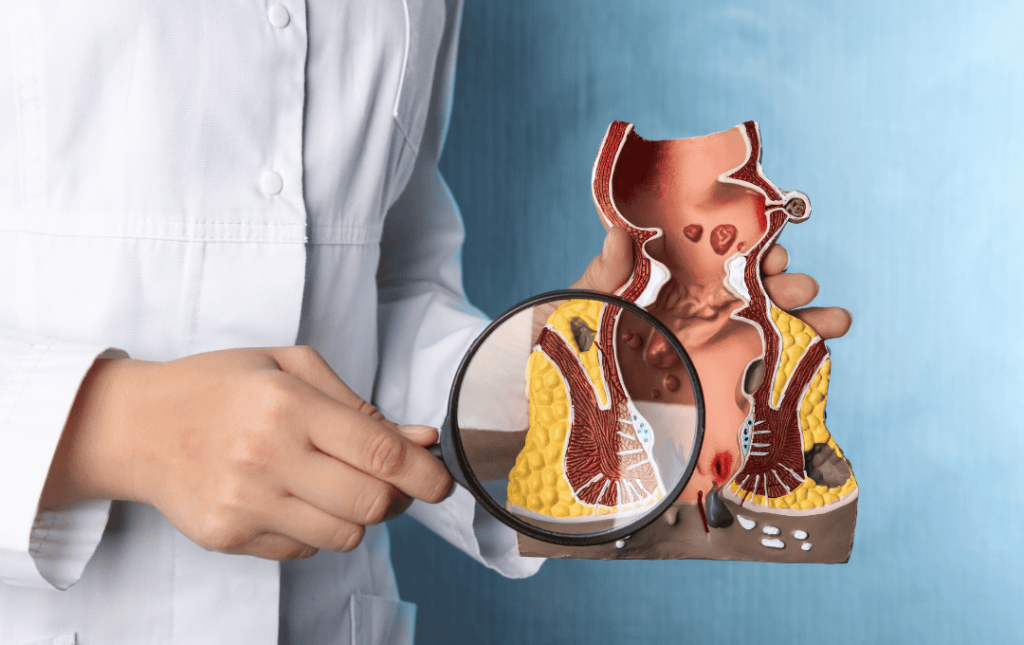
Hemorrhoids are swollen veins in the anus or lower part of the rectum.
The veins in this region expand and widen as the tissue in the rectum and anus stretches and contracts to hold and eliminate stool. Excessive stretching of these blood vessels due to pressure and straining can weaken the vein walls, causing them to become swollen and inflamed.
Common causes of hemorrhoids include:
- Straining during a bowel movement
- Straining from heavy lifting
- Excess weight
- Pressure from a growing uterus during pregnancy
These swollen piles of veins can cause serious discomfort or bleeding. They can occur internally or externally.
Anal fissures are tiny cuts on the inner lining of the anus.
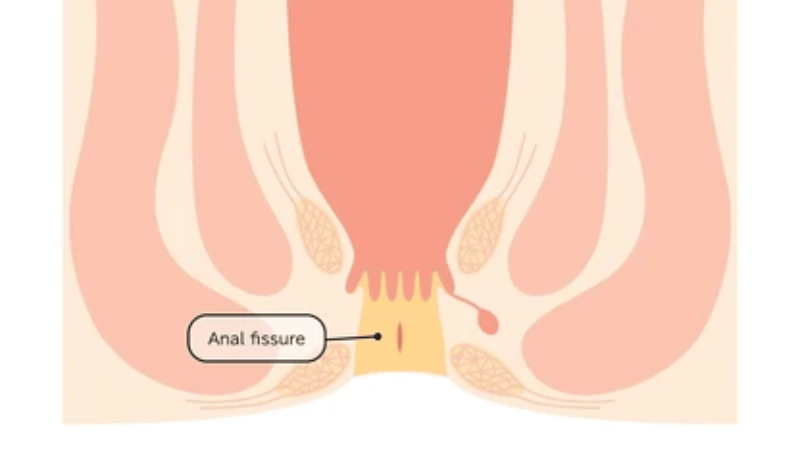
Like hemorrhoids, they can occur after straining from constipation or while passing a large or hard stool. Other possible causes include:
- Tight sphincter muscles
- Straining while giving birth
- Anal intercourse
- Chronic diarrhea
Hemorrhoid Symptoms vs. Anal Fissure Symptoms
Some hemorrhoid symptoms overlap with the symptoms of an anal fissure. Both conditions can cause the following:
- Bright red blood in the stool, on the toilet paper, or in the toilet bowl after pooping
- Anal pain
The main difference between anal fissures and hemorrhoids is when that pain occurs.
Anal fissures cause pain during a bowel movement. The pain can be severe, especially while pushing, and it can linger for minutes or hours after using the bathroom.
Hemorrhoid pain only occurs with an external hemorrhoid or an internal hemorrhoid that is prolapsed (a prolapsed hemorrhoid has fallen outside of the rectum). The pain occurs while sitting, whether on the toilet to have a bowel movement or in a chair.
With the types of hemorrhoids that cause pain (external and prolapsed hemorrhoids), it’s usually possible to feel a lump near the anus. An external hemorrhoid will feel like a hard lump. A prolapsed hemorrhoid is a soft lump that protrudes from the anus.
Pain during a bowel movement without a lump is more likely to be an anal fissure.
A non-prolapsed internal hemorrhoid may bleed, but it won’t create a lump you can feel or cause the intense pain associated with an anal fissure.
Another way to spot the difference is to look for other symptoms. Hemorrhoids can also cause irritation and itching around the anus and a feeling of pressure in the lower rectum.
Is It Possible to Have a Hemorrhoid and an Anal Fissure at the Same Time?

It is possible to have both at once, making it even more confusing to recognize if hemorrhoids or anal fissures are the cause of symptoms.
Straining and pressure can lead to swollen veins and tears in the lining of the anus. These conditions can also both be exacerbated by poor blood flow to the anal area.
The tearing from an anal fissure can cause intense pain, causing the muscles in this area to spasm, which decreases blood flow.
Studies show that people with chronic constipation and hemorrhoids are also more likely to have chronic venous insufficiency, a condition that causes varicose veins and poor blood flow.1
Poor circulation slows down the movement of oxygen and nutrients to tissue throughout the body, inhibiting the healing process.2
That’s one reason why a proper diagnosis, treatment, and lifestyle changes to prevent future problems are so important. If either one of these anal issues becomes chronic, healing can take longer, and recurrences are more likely, which means more bleeding, pain, and discomfort.
Hemorrhoid vs. Anal Fissure Treatment and Prevention Strategies
Many cases of hemorrhoids or anal fissures resolve after a few days without medical treatment. Although the causes are different between hemorrhoids and anal fissures, they both can improve from some of the same strategies. Usually, lifestyle changes help speed healing and prevent future issues.
- Eating a high-fiber diet and drinking more water can soften the stool and prevent constipation, resulting in less straining.
- Getting regular exercise increases circulation, helping to heal a tear or a swollen vein. Exercise also prevents constipation.
- Soaking in warm baths can also increase blood flow to the anal region, helping to relieve discomfort, speed healing, and prevent hemorrhoids and anal fissures.
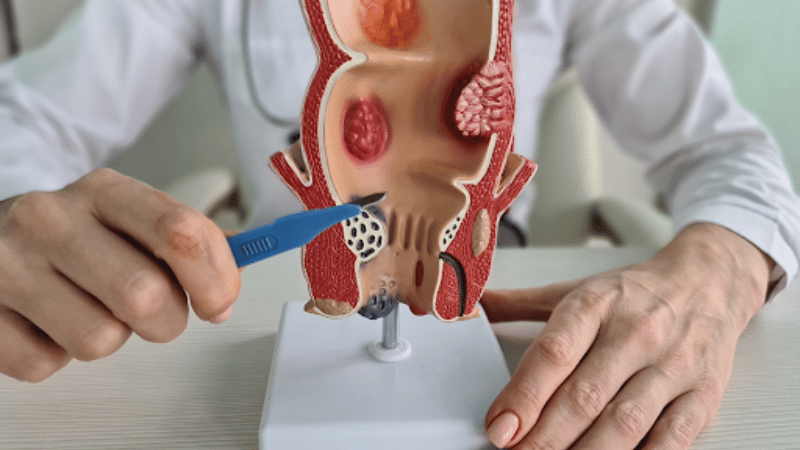
Sometimes, internal hemorrhoids don’t go away on their own and require medical treatment. They can last for weeks or longer.
Generally, hemorrhoid symptoms that don’t go away after a week should be checked out by a doctor. They can determine if someone has hemorrhoids, anal fissures, or other conditions that can cause rectal bleeding and anal discomfort, like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) or ulcerative colitis. A hemorrhoid doctor can also recommend the best treatment for the individual.
While colorectal surgeons and gastroenterologists are more commonly associated with treating hemorrhoids, Interventional Radiologists (IR) can offer effective treatments for these conditions.
IRs use minimally invasive imaging techniques to guide procedures, often providing a less invasive and faster recovery time than traditional surgical approaches.
If you’re considering treatment for hemorrhoids, it’s a good idea to discuss your options with both an IR and a colorectal surgeon or gastroenterologist to determine the best approach for your specific situation.
Hemorrhoid treatment can relieve bleeding, swelling, and other symptoms. USA Hemorrhoid Centers offers a non-surgical treatment called hemorrhoid artery embolization (HAE). This minimally invasive procedure is less painful and has a lower risk of complications than other treatments like hemorrhoid surgery and rubber band ligation, making it a good option for most people who need treatment.
Anal fissures usually go away with a high-fiber diet and drinking more water. Over-the-counter stool-softening products and fiber supplements can also help. When anal fissures are chronic, they can be treated with a sphincterotomy, a procedure that relaxes the muscles around the anus.
How to Tell if You Have Hemorrhoids or Anal Fissures?

If you’re dealing with bleeding, pain, and discomfort during or after a bowel movement, it could be hemorrhoids or anal fissures. Knowing the differences between the symptoms can help you understand what type of anorectal issue you’re dealing with. However, a proper diagnosis is the only way to know for sure and to get access to treatment for problems that won’t go away.
Why Choose USA Hemorrhoid Centers
Our doctors are experienced IR hemorrhoid specialists who can evaluate your symptoms, determine the cause, and how to treat them. We offer hemorrhoid consultations and treatment to help our patients return to living hemorrhoid-free.
If you suspect you have hemorrhoids and your symptoms don’t clear up in a few days, schedule a consultation at a location near you. We have clinics nationwide, and all of our locations accept a wide range of insurance.
Schedule a consultation with one of our expert hemorrhoid doctors and get a personalized treatment plan to help you get relief.
Find a Hemorrhoid Clinic near you
Sources
- Ekici, U., Kartal, A., & Ferhatoglu, M. F. (2019). Association Between Hemorrhoids and Lower Extremity Chronic Venous Insufficiency. Cureus, 11(4), e4502.
- InformedHealth.org [Internet]. Cologne, Germany: Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG); 2006-. Overview: Chronic wounds. [Updated 2022 Aug 8].